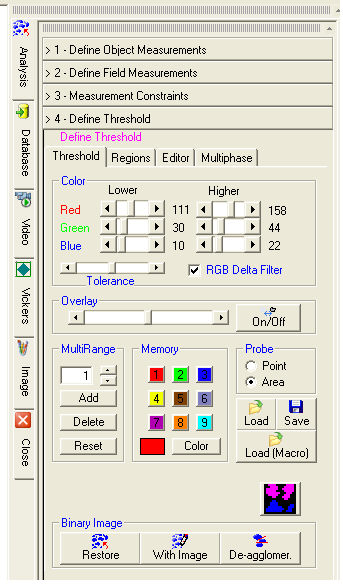
 Define Threshold
Define ThresholdA binarization is necessary to be able to analyze an image. A binarized
image is an image with two states: the active state, or the state of the
objects of interest displaying the color selected in Memory,
and the inactive state.
![]() Only the objects belonging to the colored active state will
be analyzed.
Only the objects belonging to the colored active state will
be analyzed.
The probe can be selected by Point or by Area and allows you to binarize the image by detecting the interval of color levels of the objects you need to point to and click first with the left mouse button. Several objects can be selected and each time the program updates the levels in the Color dialog and the resulting binary image.
![]() The right mouse button deletes
the last selection. To delete the whole binarization, press the Reset button.
The right mouse button deletes
the last selection. To delete the whole binarization, press the Reset button.
![]() The Zoom window, if not required, can be disabled from Zoom Window in the Measure
menu.
The Zoom window, if not required, can be disabled from Zoom Window in the Measure
menu.
The correction of the binarized image can be performed manually by using the single color scroll box or the Tolerance slider, which applies the correction to the three color components at the same time.
The binarized image consists of the areas of the image with color levels falling within the interval defined by the position of the color scroll boxes. The RGB Delta filter enters a further constraint requiring the maximum and minimum differences among the color components. This filter allows you to improve the binarization in certain situations.
This powerful function allows you to obtain a binarized image very similar to the one required. It can happen that during the normal binarizing procedure parts of the image that should not be binarized actually fall within the color interval.
For example, in the first image the two blue points represent the binarization required but the result is the one in the second image, where a large area is binarized.
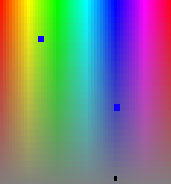

The MultiRange function can
solve this frequent problem. During
binarization, when the problem comes up, cancel the selection with the
right mouse button and press Add
in the MultiRange group box. Then continue the binarizing procedure and
repeat the MultiRange operation, if necessary up to a maximum of 100 times.
The final binary image will be very similar to the one required.
![]() Each Add operation in multirange is more demanding on the system
in terms of CPU and memory.
Each Add operation in multirange is more demanding on the system
in terms of CPU and memory.
Allows you to make the binary image transparent in order to see the original image and evaluate the degree of binarization reached. The On/Off switch enables/disables the function and the slider allows you to adjust the level of transparency.
Nine memories are available with as many colors for the multiphase analysis
of the image. A phase representing a type of object or material can be
associated with each memory. Once the binarizations for the phases of
interest have been completed, the automatic analysis can take place in
the Multiphase dialog.
![]() The Color button allows you to select the color for the current
memory.
The Color button allows you to select the color for the current
memory.
The binarization levels of all the phases can be saved and restored with Save and Load.
Load (Macro)
Allows you to load automatically a threshold configuration during the
runnung of a macro. Use this button during the recording of a macro to
select a threshold configuration to be used. By using the Load
button instead of Load (Macro),
the running of the macro will be interrupted and you will be asked to
select the configuration file to be used.
The ![]() button starts the scanning phase or image analysis
for the Current Memory.
At the end the Results: All
Objects dialog is displayed.
button starts the scanning phase or image analysis
for the Current Memory.
At the end the Results: All
Objects dialog is displayed.
Restore: restores the original binary image without the changes, if any, made with the Editor.
With Image: displays the current binary image with the original image in the background and with the changes, if any, made with the Editor.
De-agglomerate: activates the separation of the objects, which on the binary image appear touching each other.
